Mendocino Images
- Mendocino Channel Perspective View
- Mendocino Ridge and Fracture Zone
- Mendocino Volcanic Pile
- Mendocino J-Structures
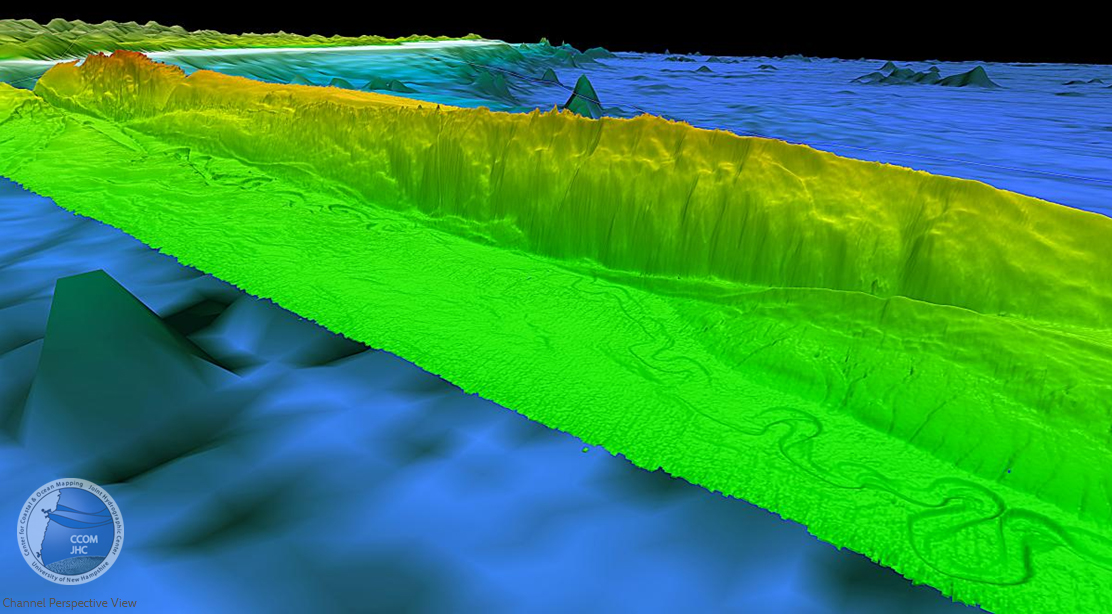
1. Mendocino Channel Perspective View
The channel meanders on the flat basin floor adjacent to the Mendocino Ridge. The channel is generally about 500 m wide and incised about 50 m deep. The section of the channel mapped is 136 km long following the channel. Vertical exaggeration 5x, looking SE.
2. Mendocino Ridge and Fracture Zone
Perspective view looking west along the Mendocino Ridge and Fracture Zone. The flat basin floor to the north (green and blue colors on right side in image) is a thickly sedimented region of young (~2 Ma) Pacific Plate created at the Gorda Ridge. The basin floor to the south (blue color on right side of image) is ~33 Ma Pacific Plate. Vertical exaggeration 5x, looking W.
3. Mendocino Volcanic Pile
Perspective view of large volcanic field located on the south side of the Mendocino Fracture Zone. Individual volcanoes as large as 2 km in diameter, some with summit calderas as much as 50 m deep. The entire volcanic pile is 1.6 km high and represents a volume of more than 720 km3 of volcanic material. Vertical exaggeration 5x, looking N.
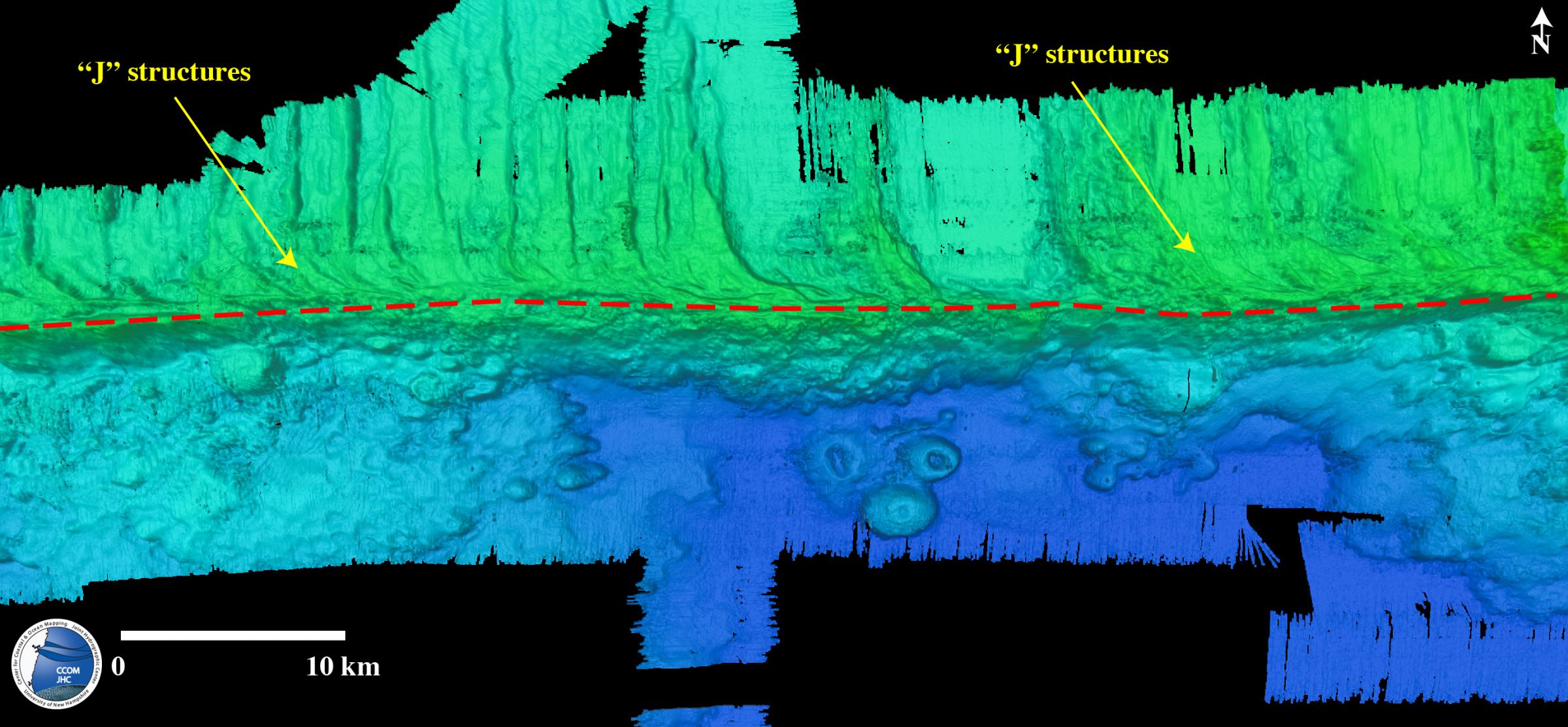
4. Mendocino J-Structures
Map view showing J-structures on relatively unsedimented ~3 Ma old section of the Pacific Plate generated at Gorda Ridge (north of red dashed line) that is moving west ~4.3 cm/yr relative to the much older (~33 Ma old) section of the Pacific Plate to the south of the red dashed line. The J-structures are formed by a reorientation of the stress field at Gorda Ridge from tensional to shear as the fracture zone is approached. The older section to the south is covered by fields of volcanic flows and volcanic cones.